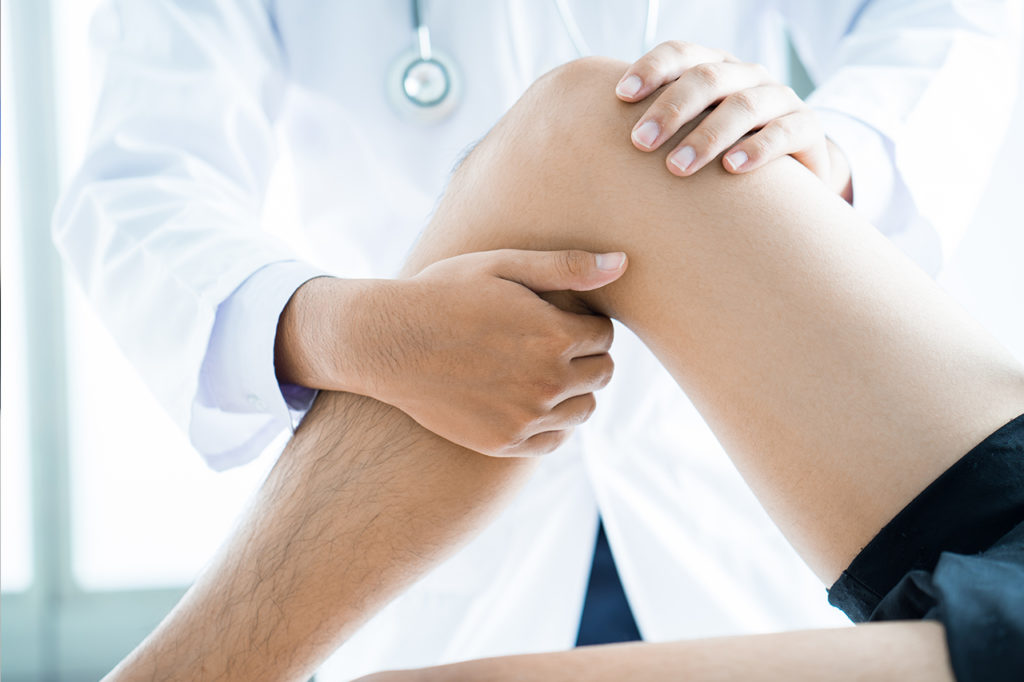
While every patient and every condition is different there are many common tests that orthopaedic surgeons use in examining a patient and coming to a diagnosis.
In general, the orthopaedic evaluation usually consists of:
- A detailed history
- Physical examination
- X-rays
- Additional tests, as needed
Your medical history is taken to assist the orthopaedic surgeon in evaluating your overall health and the possible causes of your bone and joint pain.
Physical examination — which includes examination of the individual bone or joint and the impact it has on your functioning. Special physical tests for individual joint are also carried. The surrounding structures which may have a bearing on your pain are also examined.
After the physical examination, X-ray evaluation is usually the next step in making the diagnosis. The X-rays help show how much joint damage or bony abnormality.
Occasionally, additional tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis. Laboratory testing of your blood, urine, or joint fluid can be helpful in identifying specific types of arthritis and in ruling out certain diseases. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or CT Scan or a bone scan may be needed to determine the condition of the affected bone or joint.
If you could note down the following questions and know the answers to them it shall help your orthopaedic surgeon in arriving at your diagnosis:
- Where is my pain and when do I have it?
- What is the duration of the pain?
- Is there any cause that started the pain, like injury, accident, lifting of heavy weights, travelling etc?
- How is the pain affecting my daily life and work?
- Am I on any medications?
